Reference
Streamfold Expression Language (SEL)
Introduction
The Streamfold Expression Language (SEL) is a simple and powerful free-text expression language used to construct filters for streams and functions. Expression are evaluated against individual events, resulting in a boolean value of true or false for filtering.
Anatomy of a Streamfold Expression
Streamfold expressions compose conditions. Conditions may be chained together using logical && and || operators. Expression conditions are composed of selectors, comparison operators, and literals. Let's take a look at an example.
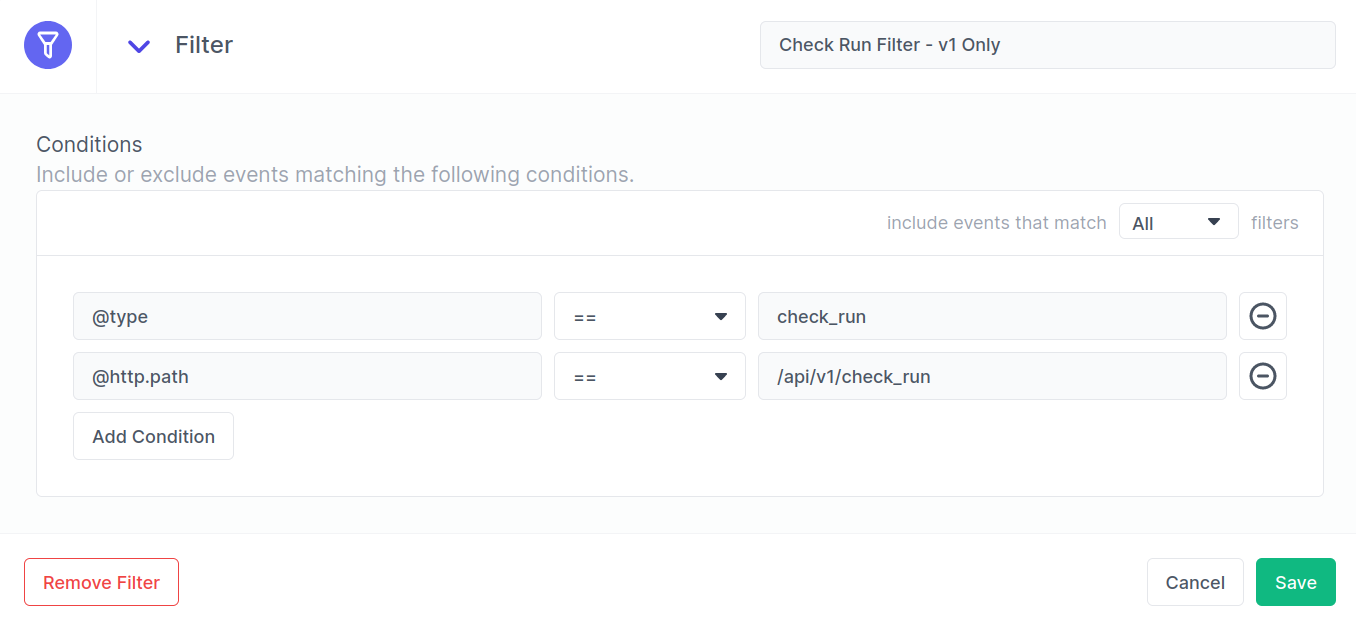
Under the hood the Streamfold expression interpreter converts these basic conditions into the following expression:
{@type} == "check_run" && {@http.path} == "/api/v1/check_run"
If we wanted the filter to pass if either of these conditions were true (||), we can change the filter to include events that match Any.
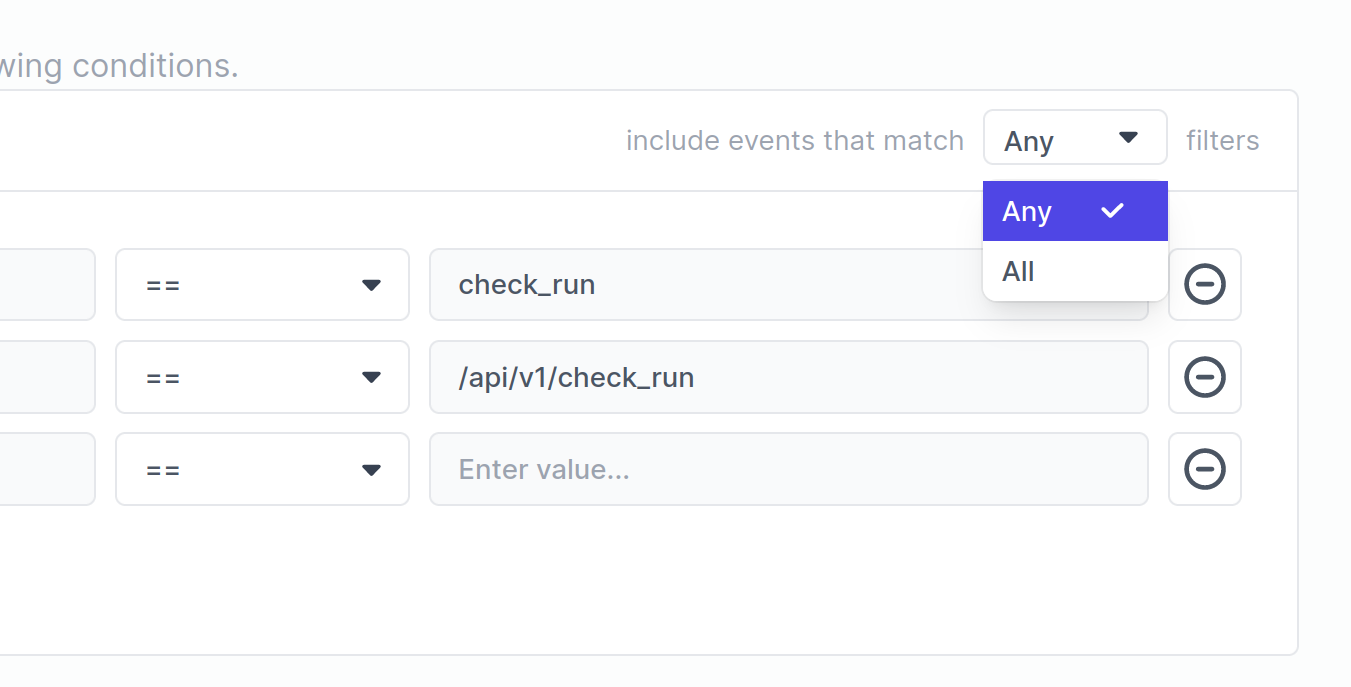
Under the hood this results in the following expression:
{@type} == "check_run" || {@http.path} == "/api/v1/check_run"
Expression Evaluation
When a filter is created the following occurs.
- The filter conditions are converted into a free-text expression.
- A new SEL interpreter is created for the filter.
- The expression is lexed, parsed, and checked for correctness.
- Finally, the expression is converted to an abstract syntax tree and is ready for evaluation.
Each time a filter receives an event, the event is passed to the SEL interpreter. The interpreter fetches the actual values from the event specified by your selectors and evaluates the rest of the expression.
Data Types
The following is the list of data types supported by the Streamfold expression language.
| Type | Notes |
|---|---|
| bool | true or false |
| string | [] utf-8 encoded bytes |
| integer | signed 64-bit integer |
| double | signed 64-bit IEEE-754 floating point number |
| map | keys are string, values may be any of supported types |
| array | array of any supported type |
| undefined | reserved type representing a map key is not present |
| matcher | used in rhs of matches expression, may be string with wildcard, or regular expression surrounded by // |
| nil | nil |
Comparison Operators
| Type | Identifier | Data Types | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| equals | == | all | |
| not equals | != | all | |
| greater than | > | string, integer, double | |
| greater than or equal to | >= | string, integer, double | |
| less than | < | string, integer, double | |
| less than or equal to | <= | string, integer, double | |
| contains | contains | string, map, array | For string performs substring match, containers exact match |
| matches | matches | string | Supports wild card matching or a regular expression if wrapped in // |
Nil and Undefined
Expression may include comparisons to nil, as in some cases source payloads may contain literal nil or null values. However, attempting to access a variable via a selector path that doesn't exist returns undefined rather than nil. This is to allow users to differentiate between a literal nil and whether a field exists or not.
Comparing Integers and Doubles, and Implicit Conversion
For convenience, when comparing integers and doubles, integers are automatically converted to doubles. Other than integer to double conversion, no other implicit conversions occur. Therefore, if the two types of values being compared are not identical, all equality and greater than, less than, comparison operations will return false.